The Glycemic Index (GI) measures how carbohydrates & sugars affect your blood glucose levels, helping you choose foods to maximize your nutrition and health. Carbs & Proteins (which get broken down into sugars by your body) are the energy that run your brain, muscles and most organs.
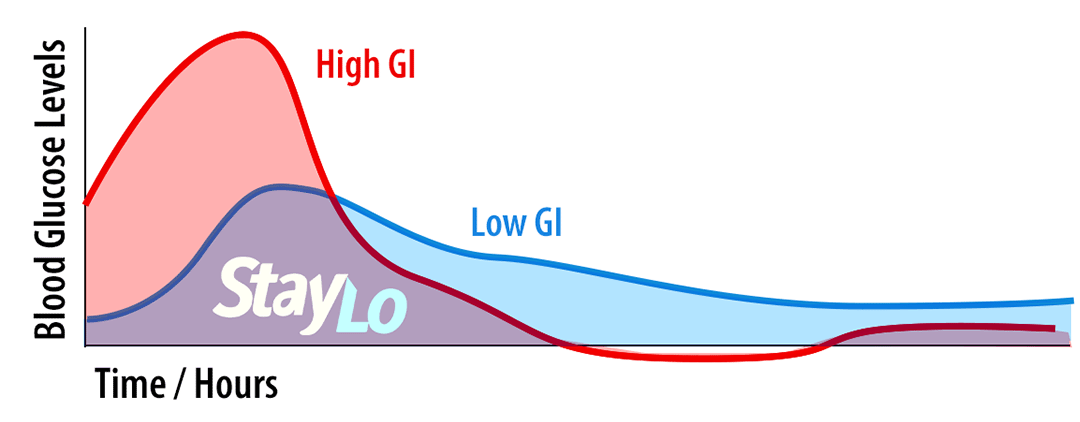
High GI carbs cause blood glucose levels to spike upward forcing the pancreas to push insulin into your body and bring blood sugar down.
Low GI carbs are digested and released slowly for sustained low blood sugar energy.
Glycemic Load combines the quantity and quality (GI) of carbohydrates providing a way to compare blood glucose values of different types and amounts of foods. How high your blood glucose rises and how long it stays high depends on load and not index.